Intro to Reactive Programming

Reactive Programming is a declarative programming paradigm concerned with data streams and the propagation of change

Propagation of change(behaviour)
a = b + c
a is automatically updated whenever the values of b and/or c change
// imperative
let a = 1;
let b = 2;
let c = a + b; // => 3;
a = 3;
c; // => 5?
// reactive
let R(a) = 1;
let R(b) = 2;
let R(c) = R(a + b); // => 3;
a = 3;
c; // => exactly! 5Observer Pattern
subscribe: adds new observable events
unsubscribe: removes observable events
broadcast(notify): executes all events with bound data
Data Stream
a stream is a sequence of data elements made available over time.
click...
click...........
click...
click......
click...........
event...
event.........
event...
event....
event.........
Data Stream
The Tool


[]
.map(fn)
.map(fn)
.filter(fn)
.anyHigherOrderFunctionHere(fn)

*RxJS
RxJS Concepts(keywords)
- Observable: represents the idea of an invokable collection of future values or events.
- Observer: is a collection of callbacks that knows how to listen to values delivered by the Observable.
- Subscription: represents the execution of an Observable, is primarily useful for cancelling the execution.
- Operators: are pure functions that enable a functional programming style of dealing with collections with operations like map, filter, concat, flatMap, etc.
- Subject: is the equivalent to an EventEmitter, and the only way of multicasting a value or event to multiple Observers.
- Schedulers: are centralized dispatchers to control concurrency, allowing us to coordinate when computation happens on e.g. setTimeout or requestAnimationFrame or others.
Observable
Lazy Push collection of multiple values
Push
vs
Pull
decides when data is requested
reacts to received data
Systems
Wrap
// From one or multiple values
const $x = Rx.Observable.of('foo', 'bar');
// From array of values
const $x = Rx.Observable.from([1,2,3]);
// From an event
const event = document.querySelector('button');
Rx.Observable.fromEvent(event, 'click');
// From a Promise
const $x = Rx.Observable.fromPromise(fetch('/users'));
// etcCreate
const $x = Rx.Observable.create(o => {
o.next('Hello!');
o.error('Ooops!');
o.complete();
});If either an error or complete notification is delivered,nothing else can be delivered afterwards.
Observer
Subscribe
$x.subscribe(
n => console.log(n),
e => console.log(e),
() => console.log('complete')) A subscribe call is simply a way to start an "Observable execution" and deliver values or events to an Observer of that execution.
$x.subscribe({
next: i => {code here}
error: e => {code here}
complete: c => {code here}
});Unsubscribe
const $a = Rx.Observable.from([10, 20, 30]);
const subscription = $a.subscribe(x => console.log(x));
// Later:
subscription.unsubscribe();Unsubscribe(Angular's component)
public subscriptionList;
constructor() {}
public ngOnInitOrAnyOtherMethod {
const observableSubscription =
this.$observable.subscribe();
this.subscriptionList.push(observableStateSubscription);
}
public ngOnDestroy() {
this.subscriptionList.forEach(
subscription => subscription.unsubscribe()
);
}Subject
It's Observable but can multicast to any Observers
const subject = new Rx.Subject();
subject.next(1);
subject.next(2);
subject.subscribe({
next: (v) => console.log('observerA: ' + v)
});
subject.subscribe({
next: (v) => console.log('observerB: ' + v)
});
subject.next(3);
subject.next(4);
subject.next(Math.random());
//Result
// "observerA: 3"
// "observerB: 3"
// "observerA: 4"
// "observerB: 4"
// "observerA: 0.47454296336548896"
// "observerB: 0.47454296336548896"
Operators
operator(observable) => observable
Creation Operators
Transformation Operators
Filtering Operators
Combination Operators
Multicasting Operators
Error Handling Operators
Utility Operators
Conditional and Boolean Operators
Mathematical and Aggregate Operators
Categories:
"Think of RxJS as Lodash for events"
Map
transformation
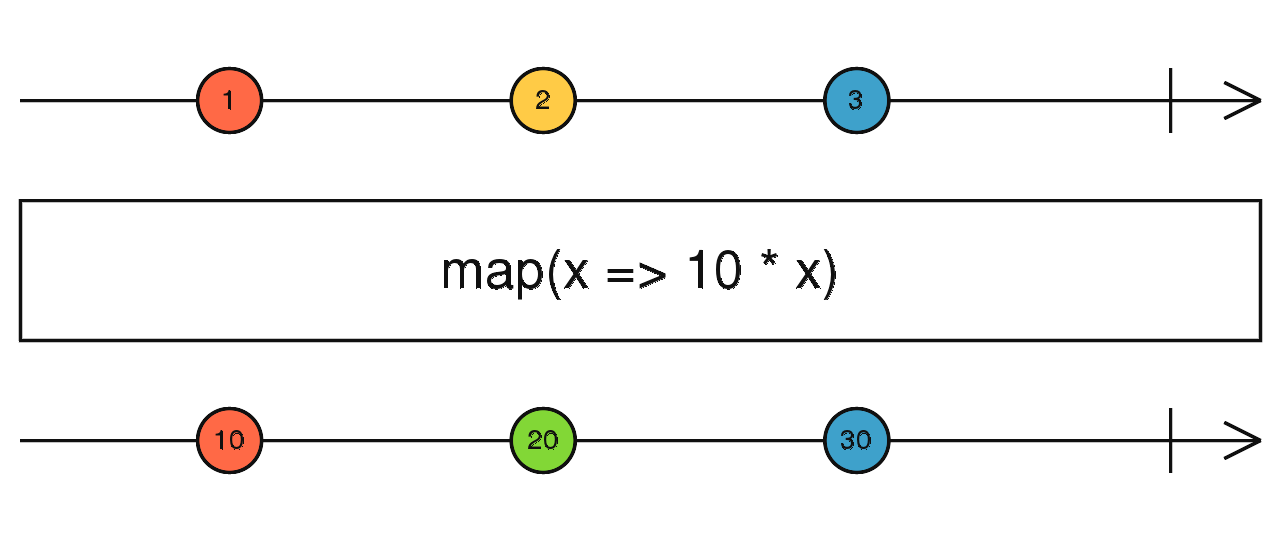
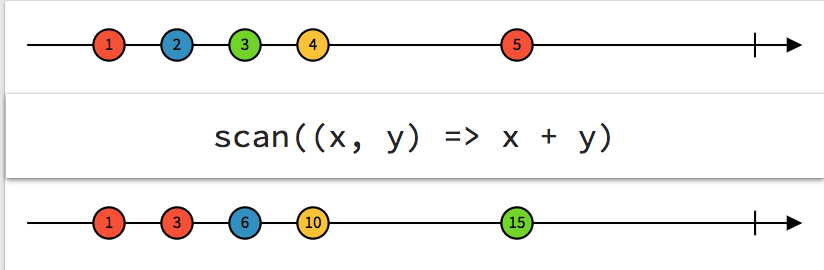
Scan
accumulation
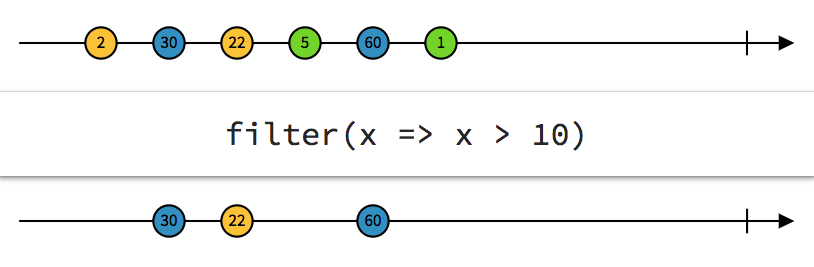
Filter
filtering
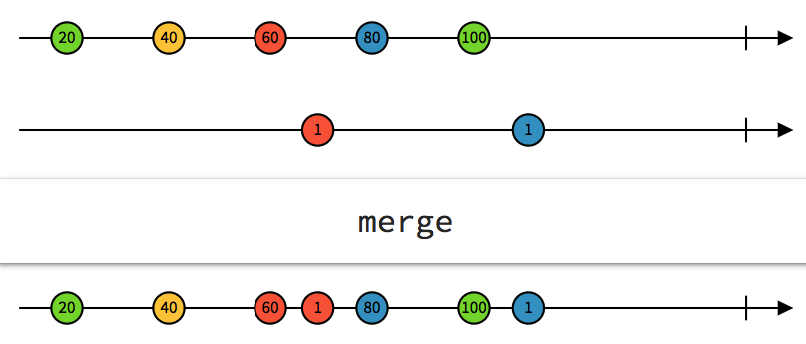
Merge
flattens multiple Observables together
Materials
Q&A